


Categories: Peptide Finished product, Peptides and Their Dosages
Free (1) 30 ml Bacteriostatic Water
with qualified orders over $500 USD.
(excludes capsule products, cosmetic peptides, promo codes and shipping)
GHRP-6 is a synthetic ghrelin/growth hormone secretagogue agonist. It has positive effects on appetite, heart muscle cells, scar formation, and sexual motivation. Animal studies show this orally active growth hormone secretagogue also improves memory function and may help to thwart the neurological effects of Parkinson’s disease.
Product Usage: This PRODUCT IS INTENDED AS A RESEARCH CHEMICAL ONLY. This designation allows the use of research chemicals strictly for in vitro testing and laboratory experimentation only. All product information available on this website is for educational purposes only. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law. This product should only be handled by licensed, qualified professionals. This product is not a drug, food, or cosmetic and may not be misbranded, misused or mislabled as a drug, food or cosmetic.
GHRP-6 is an effective stimulator of natural Growth Hormone Release from the anterior pituitary. GHRP-6 is also a ghrelin/growth hormone receptor agonist and one of a handful of ghrelin analogues developed in the last several decades. It has been found to have positive effects on heart muscle cells, memory formation, scar formation, sex motivation, and the neurons involved in Parkinson’s disease. GHRP-6 is orally and sublingually active and moderately to highly selective.
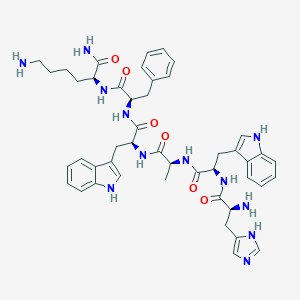
Sequence: His-D-Trp-Ala-Trp-D-Phe-Lys
Molecular Formula: C46H56N12O6
Molecular Weight: 873.032 g/mol
PubChem CID: 9919153
CAS Number: 87616-84-0
The role of physical activity in learning and memory formation has been under active investigation for some time now. Though the exact mechanism has remained elusive, there has always been reason to believe that physical activity improves cognition and learning, particularly when exercise is done immediately following a learning task.
Originally, the benefit of exercise on cognition was chalked up to improved blood flow and vague references to growth hormone (GH). Research in rodents has helped to clarify why GH may be an important factor in memory formation by revealing that GHRP-6 can help to solidify newly formed memories and convert short-term memories into long-term storage[1], [2]. There is also strong evidence to support a role for ghrelin/GHRP-6 in spatial learning tasks[3]. This suggests that exercise-induced cognitive benefits may be mediated through growth hormone secretagogues like ghrelin and that the GH effect may be indirect and, perhaps, secondary to these peptides.
Animal models of stroke are used to investigate the ability of GHRP-6 to protect neurons and other cells in the central nervous system from the effects of poor blood supply. It turns out that GHRP-6 not only protects brain tissue during acute stroke, but can actually rescue memory deficits following a stroke if administration of the peptide is timely[4], [5]. It seems that ghrelin and its analogues inhibit apoptosis (programmed cell death) and reduce inflammation inflammation in the brain, protecting neurons from both their genetic programming and the surrounding environment following stroke.
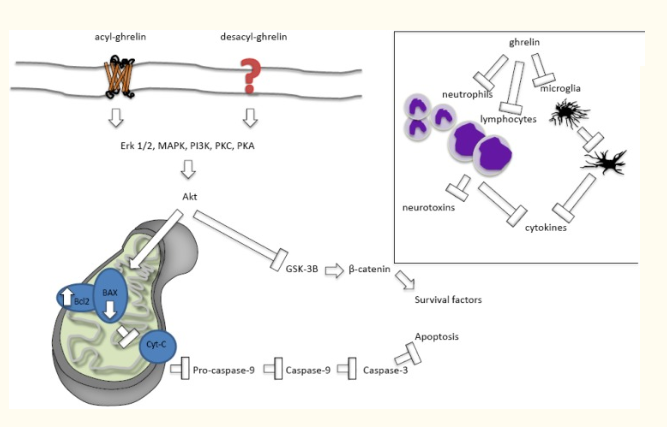
Our understanding of the ability of GHRP-6 to protect brain tissue was brought into sharper focus by a 2018 study revealing that ghrelin receptors are found in the substantia nigra, a part of the brain affected by Parkinson’s disease. Patients with known genetic links to Parkinson’s disease show a decrease in the expression of ghrelin receptors on neurons in the substantia nigra. Additionally, rats with this same defect show Parkinson’s symptoms when an antagonist is injected[6]. It stands to reason that agonists like GHRP-6 may therefore be useful in the setting of Parkinson’s. Scientists speculate that the peptide may, by binding to the diminished receptors, reduce apoptosis in neurons of the substantia nigra and slow or even prevent the onset of Parkinson’s.
GHRP-6 improves the survival of multiple types of cells by reducing programmed cell death. The peptide also interacts with the CD36 receptor, which is known to promote blood vessel growth, particularly in wounds. Research in rats indicates that these properties make GHRP-6 highly useful in wound healing where it increases the rate of wound closure, improves the formation of extracellular matrix proteins like collagen, and interferes with the normal process of scar formation to help organize overall structure at the site of the wound and reduce the appearance of scar tissue[7].
The peptide has also been found to prevent the development of hypertrophic scars. Hypertrophic scars, like keloids, are the result of improper extracellular matrix protein depositions. GHRP-6 prevents this process from occurring, which is a huge boon for people who suffer from this aberrant healing process and thus often put off surgery and other medical procedures as much as possible to avoid the painful scars that develop and cause substantial aesthetic alteration[8].
Research in porcine models of heart attack shows that GHRP-6 can prevent oxidant cytotoxicity, which is to say that peptide protects heart cells from damage by free radicals[9]. There is hope that this finding will lead to the development of drugs that can be administered following a heart attack to protect cells that are vulnerable, but still viable. Such a drug could reduce death and improve long-term outcome following heart attack.
Research in male rats indicates that ghrelin receptors in the central nervous system affect sexual behavior and motivation. Elevated levels of ghrelin, for instance, can boost sexual motivation. Research with GHRP-6 and a modified GHRP-6 designed to antagonize the ghrelin receptor has indicated that ghrelin receptors in specific brain regions help to modulate sex behavior and reward-seeking behavior[10]. These findings are not only applicable to sex and conditions like hypoactive sexual desire disorder, but may also be applicable to hunger and other types of motivation.
There is also evidence to suggest that ghrelin may impact mood as part of its effect on motivation. Research in mice indicates that GHRP-6 and other ghrelin receptor agonists can decrease depression and improve function in parts of the brain associated with mood, particularly in the setting of stress[11]. GHRP-6 could form the basis for research into potential novel treatments for stress, anxiety, depression, and other mood disorders.
GHRP-6 exhibits minimal to moderate side effects, low oral and excellent subcutaneous bioavailability in mice. Per kg dosage in mice does not scale to humans. GHRP-6 for sale at
The above literature was researched, edited and organized by Dr. Logan, M.D. Dr. Logan holds a doctorate degree from Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine and a B.S. in molecular biology.
Márta Korbonits graduated in Medicine in Budapest and undertook her early clinical training at the Internal Medicine Department of the Postgraduate Medical School, Budapest. She joined the Department of Endocrinology at St. Bartholomew’s Hospital under the mentorship of Professors Ashley Grossman and Michael Besser. Her MD and later PhD studies contributed to the understanding of the effects of growth hormone secretagogues on hypothalamic hormone release and the nature and causes of pituitary tumorigenesis. She was awarded an MRC Clinician Scientist Fellowship and commenced studies that produced novel insights into ghrelin physiology and genetics. Her findings related to the regulation of the metabolic enzyme AMPK by ghrelin, cannabinoid and glucocorticoid opened a new aspect of hormonal regulation of metabolism. In 2008, Márta Korbonits was promoted to Professor of Endocrinology and Metabolism and since 2012, has led the Centre of Endocrinology at Barts and the London School of Medicine. In 2016, Márta Korbonits was appointed a Deputy Head of the William Harvey Research Institute. Professor Korbonits continues to integrate human studies alongside with laboratory-based research and has pioneered several projects in translational medicine.
Márta Korbonits is being referenced as one of the leading scientists involved in the research and development of GHRP-6. In no way is this doctor/scientist endorsing or advocating the purchase, sale, or use of this product for any reason. There is no affiliation or relationship, implied or otherwise, between
ALL ARTICLES AND PRODUCT INFORMATION PROVIDED ON THIS WEBSITE ARE FOR INFORMATONAL AND EDUCATIONAL PURPOSES ONLY.
The products offered on this website are furnished for in-vitro studies only. In-vitro studies (Latin: in glass) are performed outside of the body. These products are not medicines or drugs and have not been approved by the FDA to prevent, treat or cure any medical condition, ailment or disease. Bodily introduction of any kind into humans or animals is strictly forbidden by law.
PeptideGurus is a leading supplier of American-made research peptides, offering top-quality products at competitive prices. With a focus on excellence and customer service, they ensure a secure and convenient ordering process with global shipping.
CONTACT